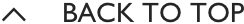The Second Key Step Towards Becoming an Autonomous Car
Autonomous Car is an innovative drive system that combines the Automated Driving Systems (ADSs) and Advanced Driver – Assistance Systems (ADAS).




What is Advanced Driver – Assistance Systems (ADAS)?
What is Advanced Driver – Assistance Systems (ADAS)?


Advanced Driver – Assistance Systems (ADAS) is an active safety system that helps prevent, avoid and reduce risks on the road. The system makes driving safer by reducing the risk of accidents and improving driver confidence.

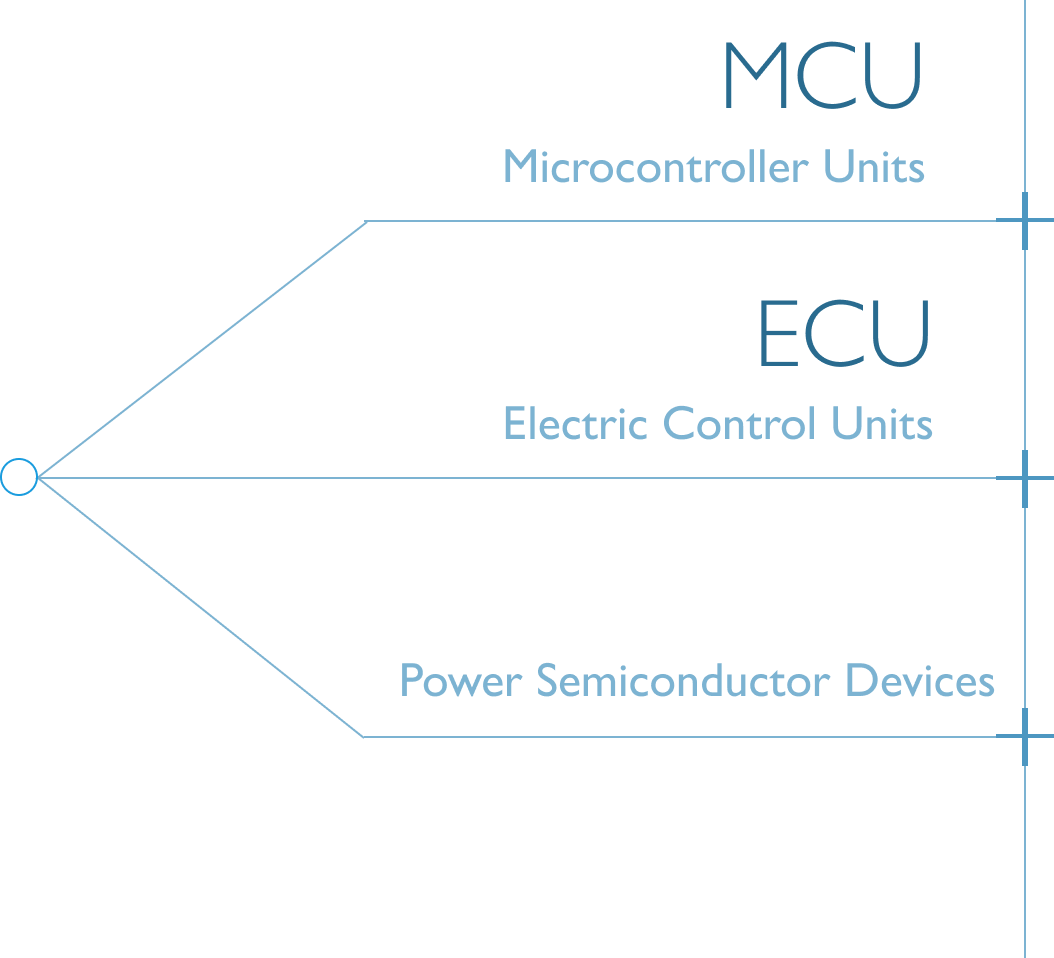
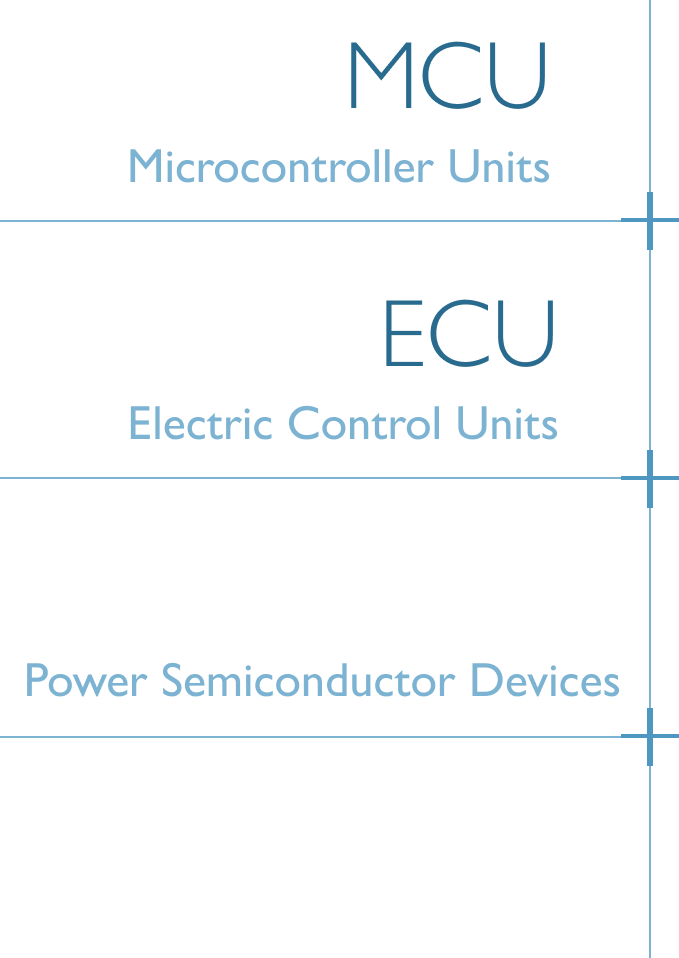
To improve the system’s overall performance, ADAS will integrate with the following electronics:
- Microcontroller Units (MCU)
- Electronic Control Units (ECU)
- Power Semiconductor Devices

ADAS mostly works to reduce human error, which is the major cause of road accidents. It also provides and improves driving confidence and safety through the various systems alarms. The system can also automatically takeover control to prevent an accident when a high risk event occurs.
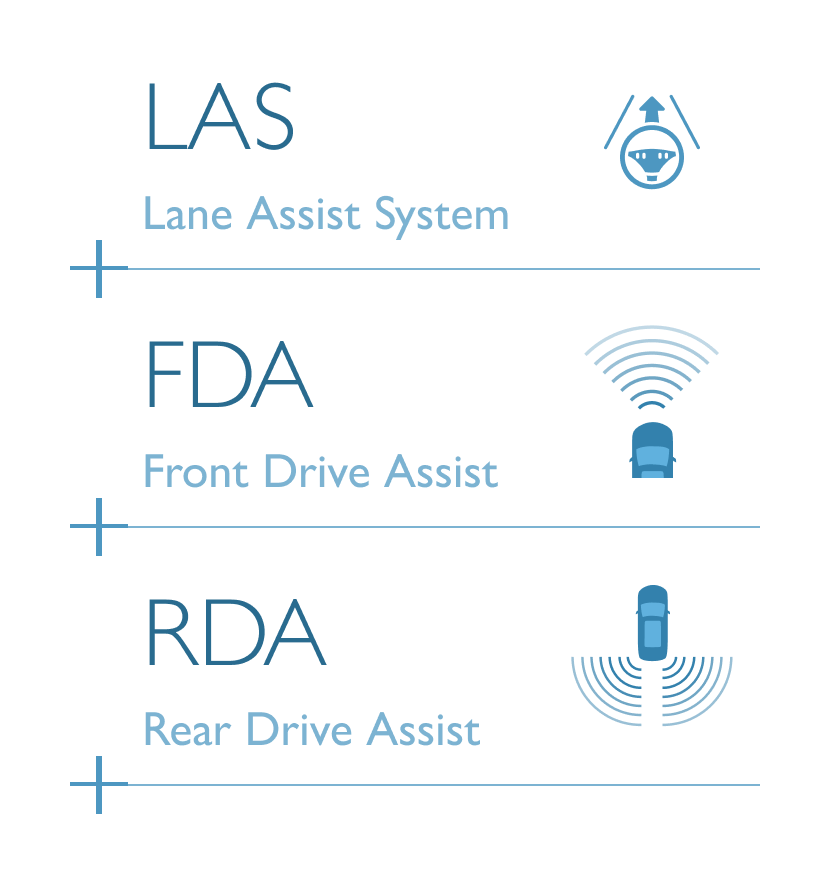
Advanced Driver – Assistance Systems (ADAS) combines advanced safety features for vehicles and drivers in 3 main systems: LAS (Lane Assist System), FDA (Front Drive Assist) and RDA (Rear Drive Assist). The feature comprises a total of 11 integrated sub-systems to help drivers feel safer and more confident on every journey.


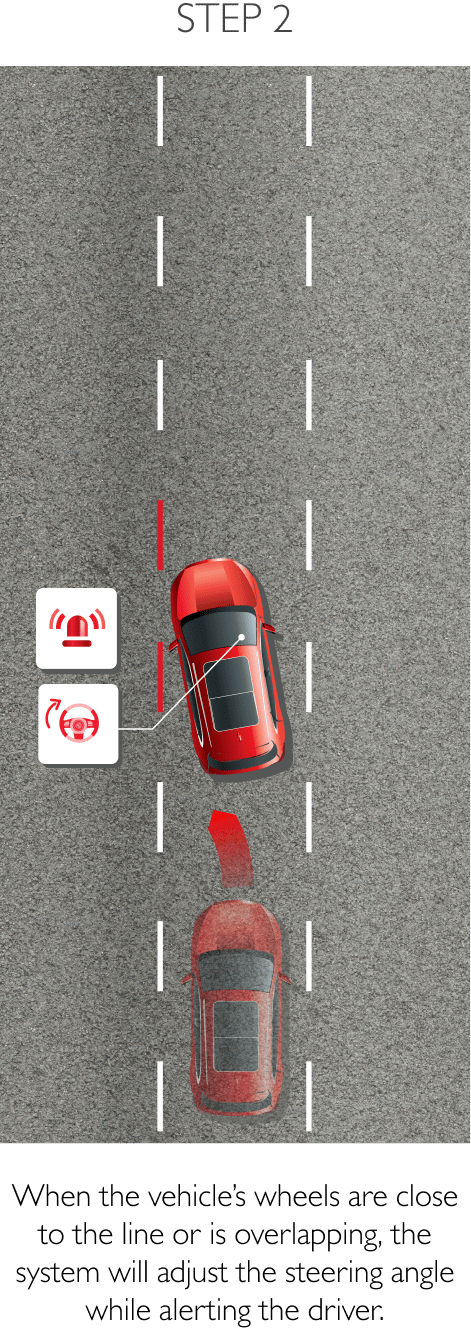
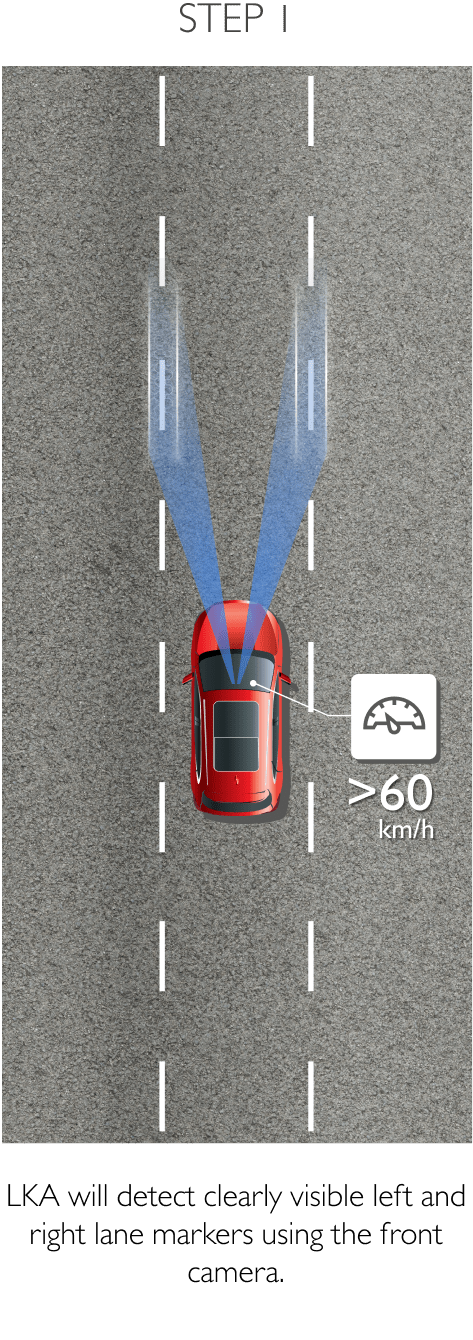
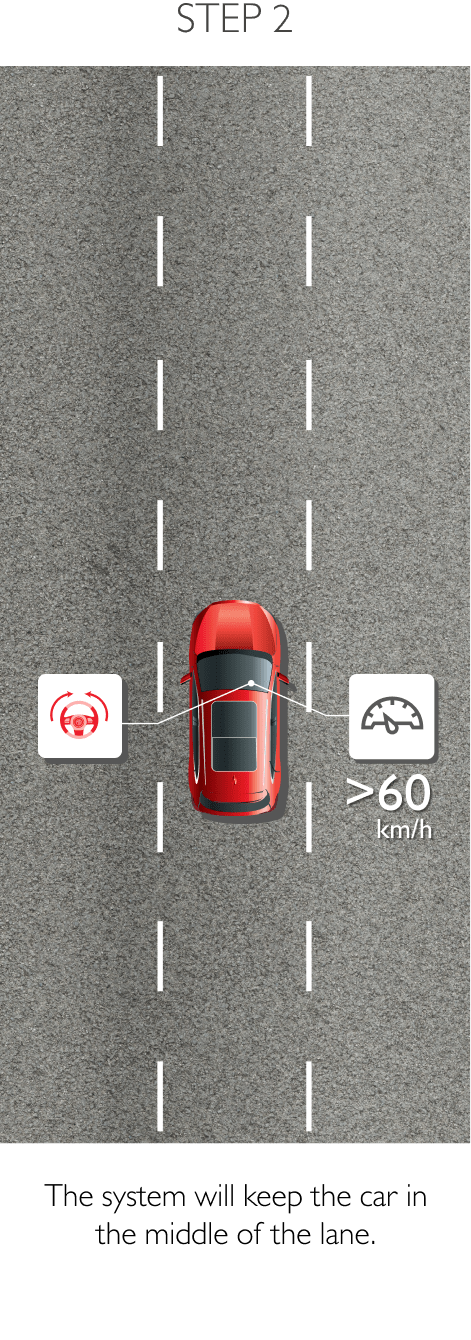
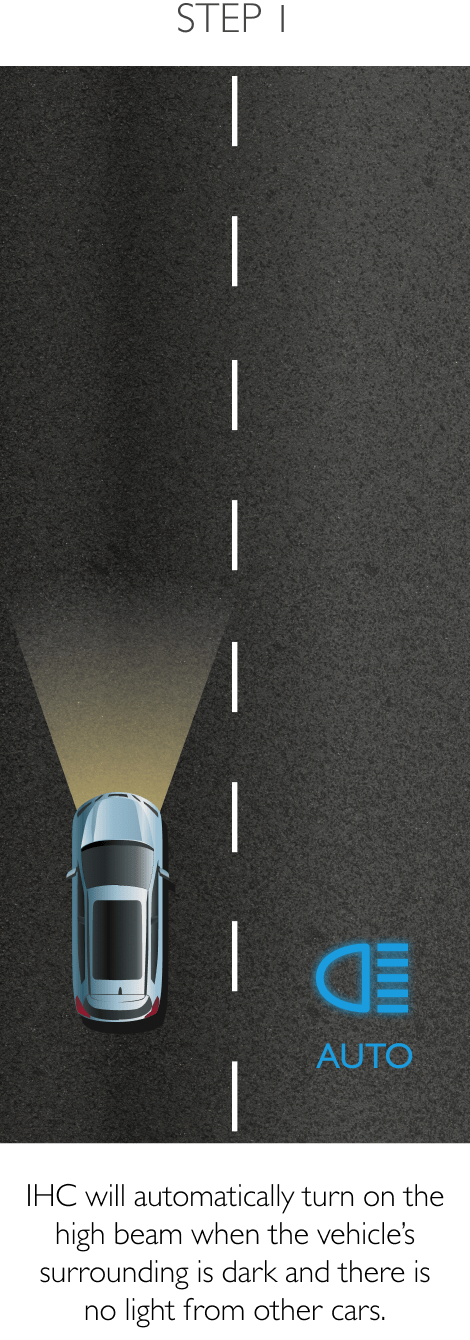
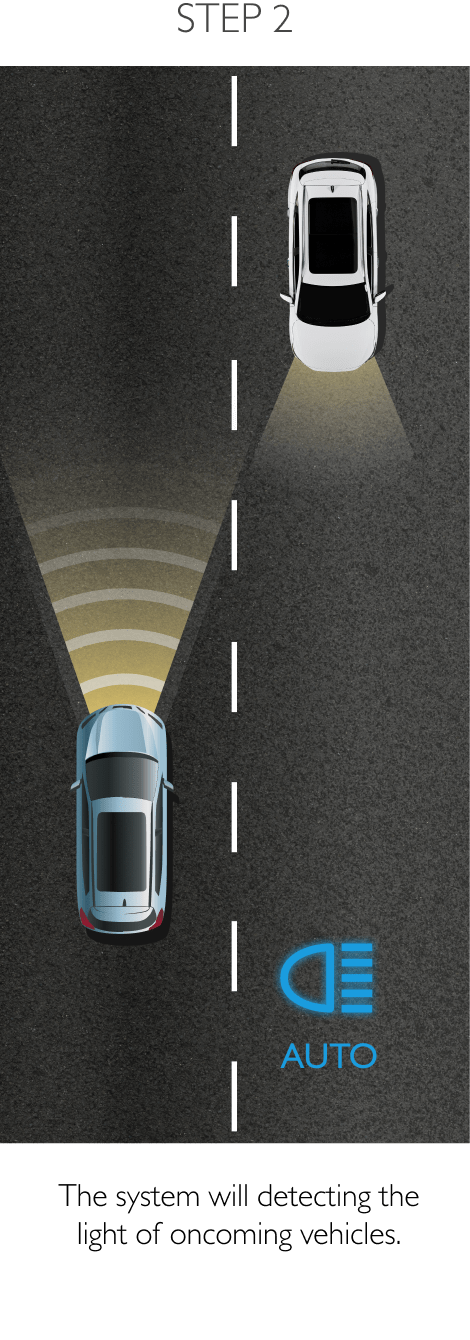
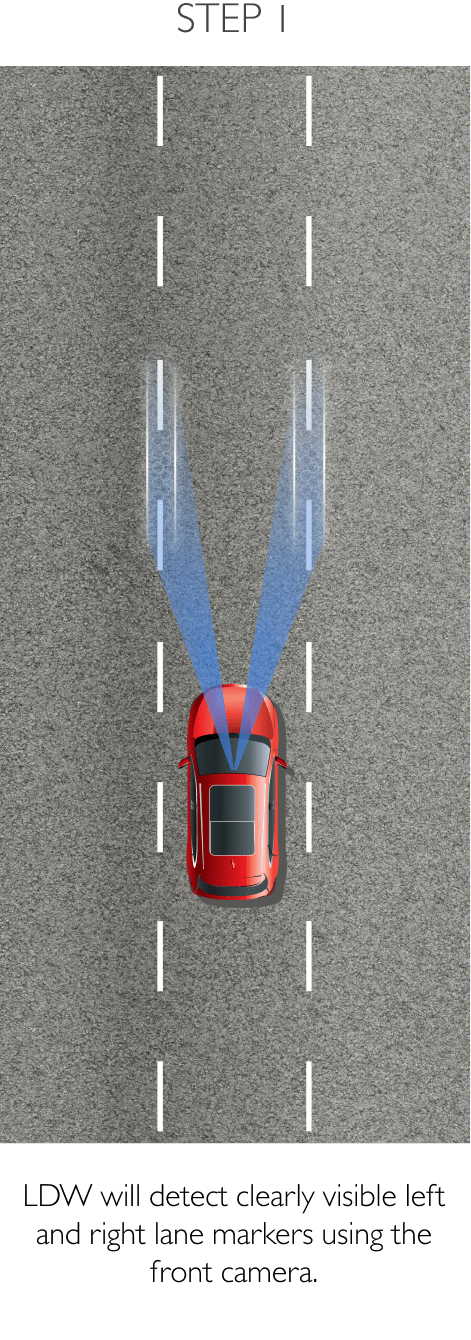
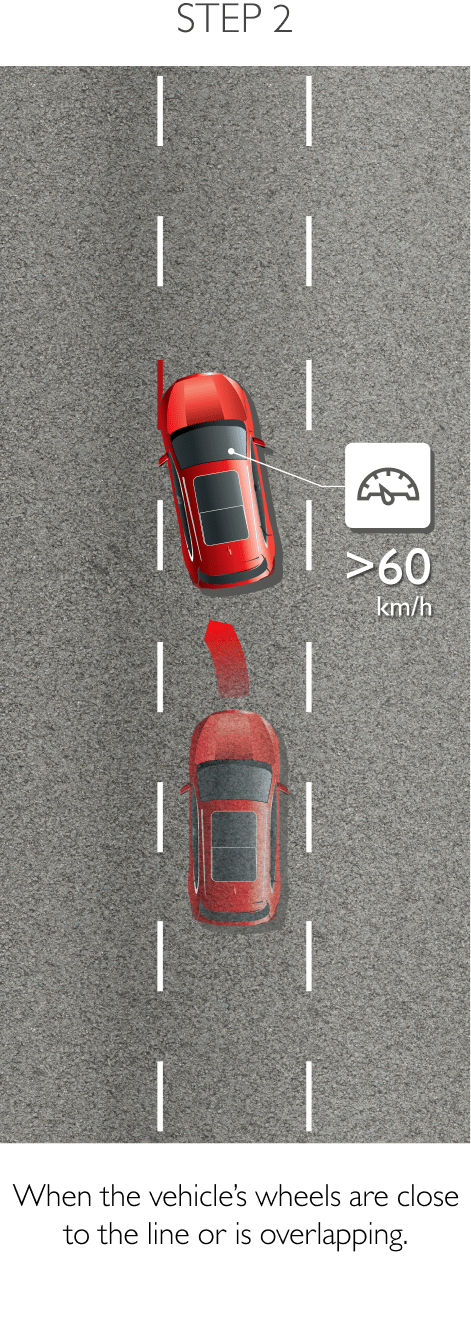
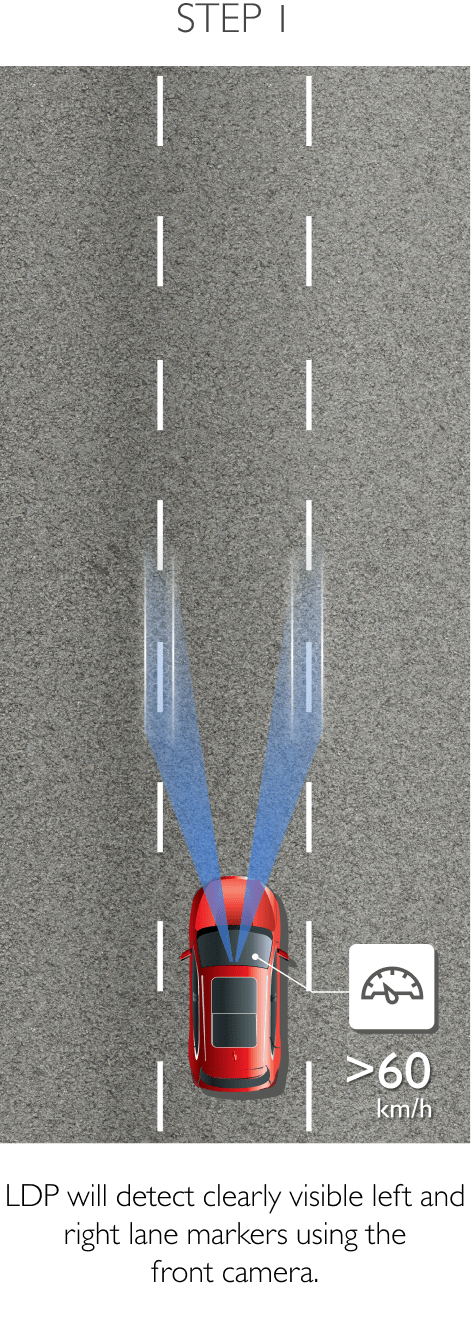
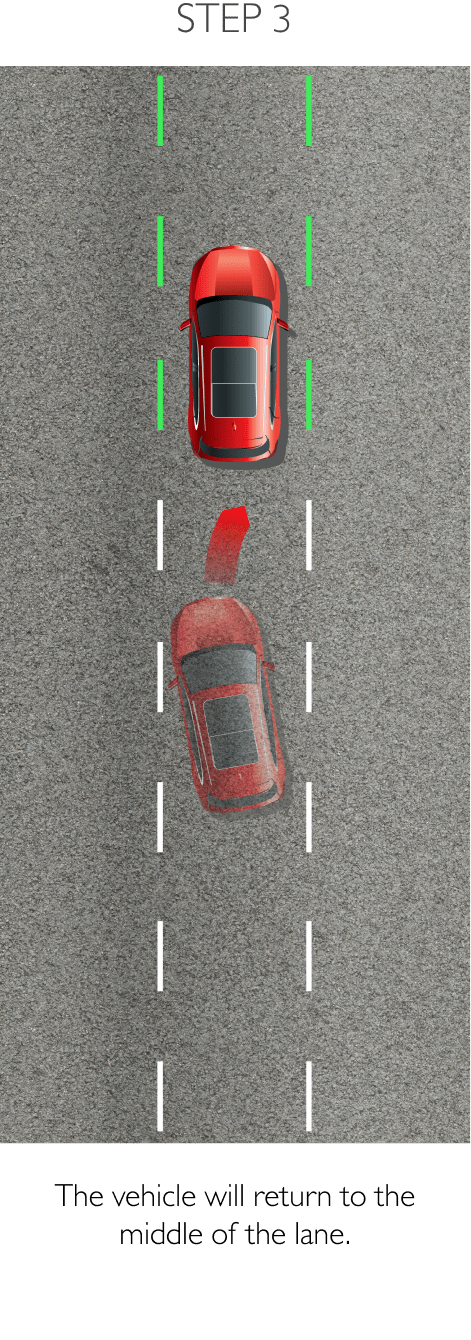
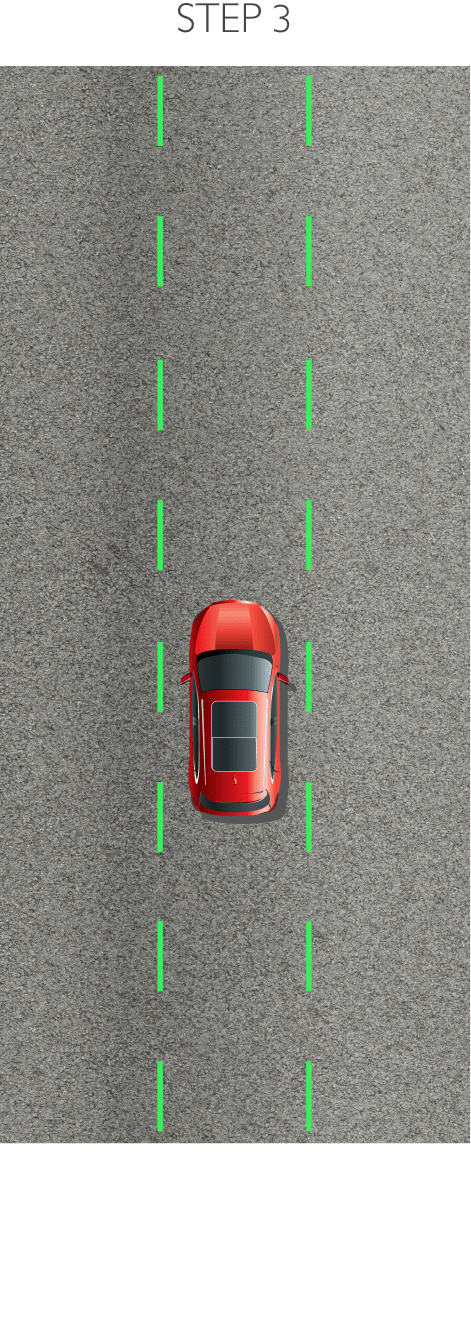
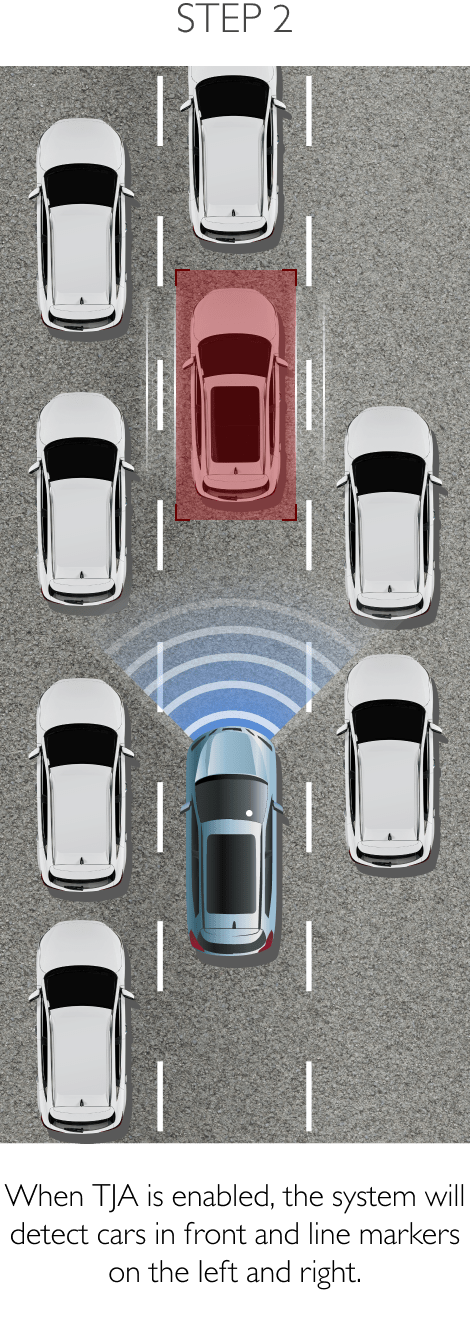
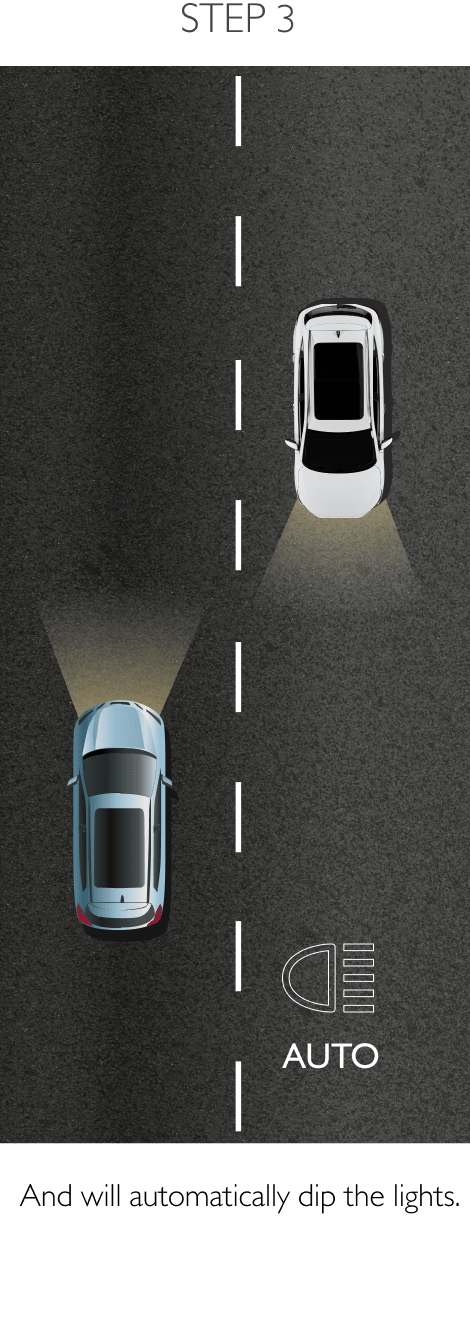
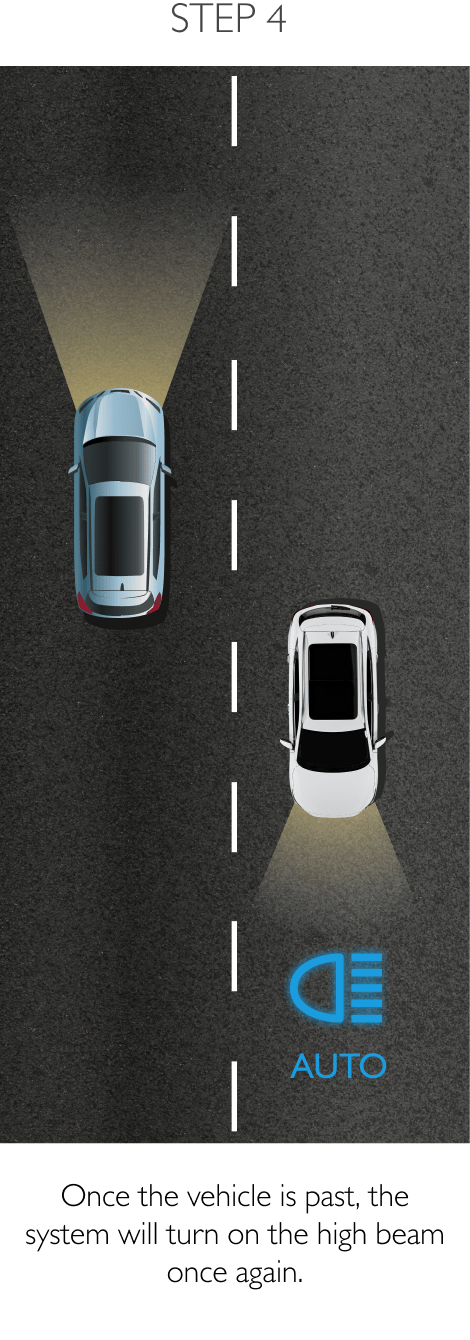
The system keeps the car safely in the centre of the lane. Using a front-mounted camera attached to the base of the rearview mirror, the system will survey its surroundings and road conditions to the front of the vehicle. When the conditions meet certain criteria, the system will alert the driver or even help control the vehicle. The system increases road safety and driver confidence using the follow 3 sub-systems.
The system keeps the car safely in the centre of the lane. Using a front-mounted camera attached to the base of the rearview mirror, the system will survey its surroundings and road conditions to the front of the vehicle. When the conditions meet certain criteria, the system will alert the driver or even help control the vehicle. The system increases road safety and driver confidence using the follow 3 sub-systems.




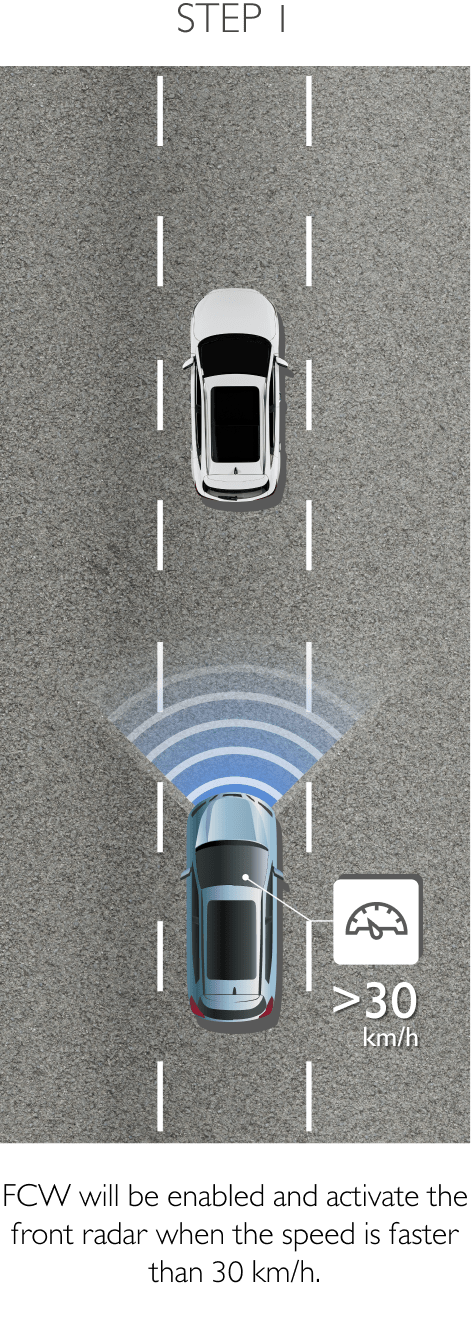
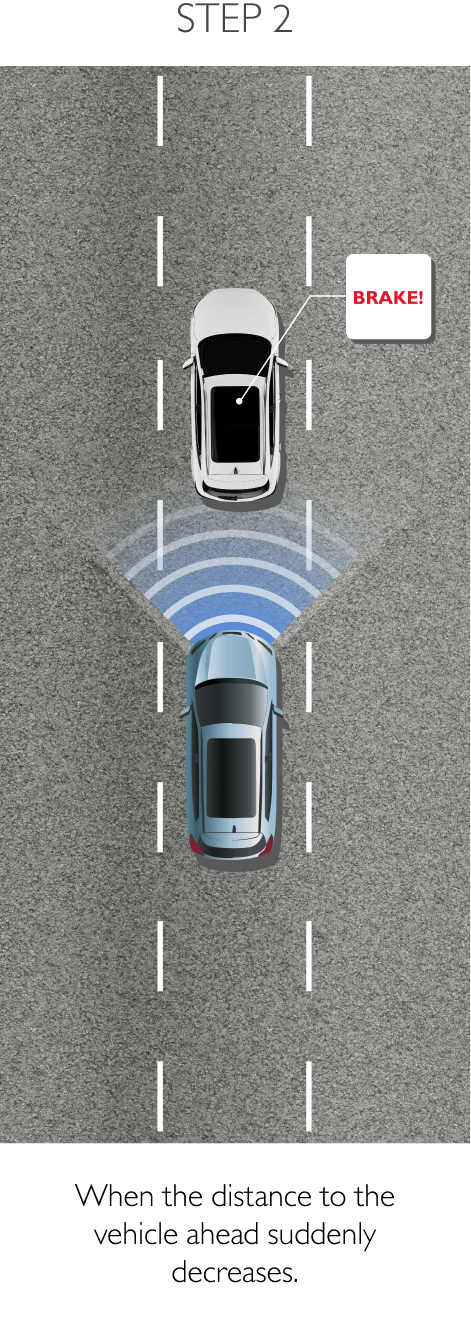
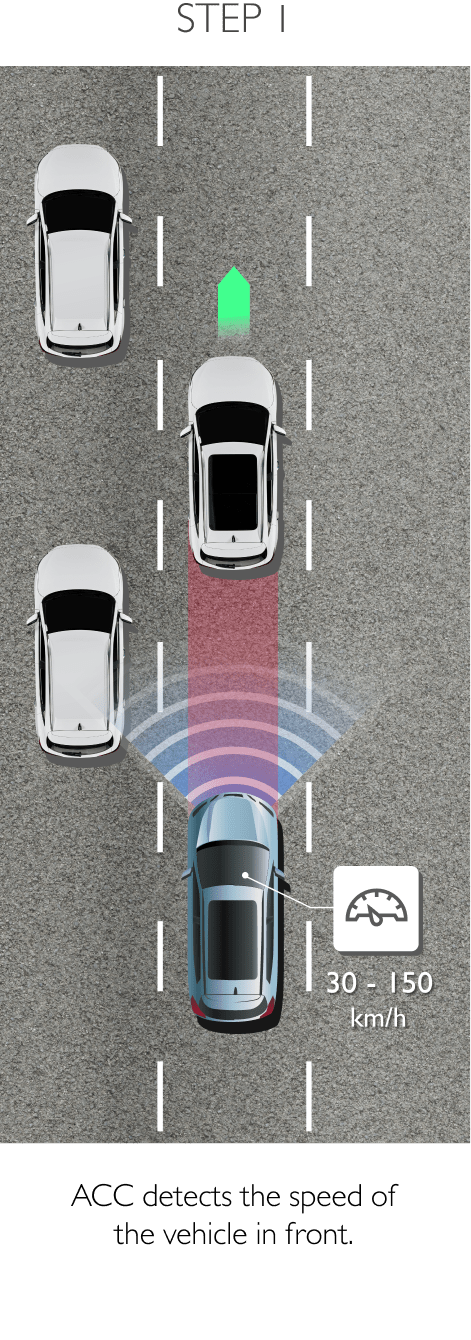
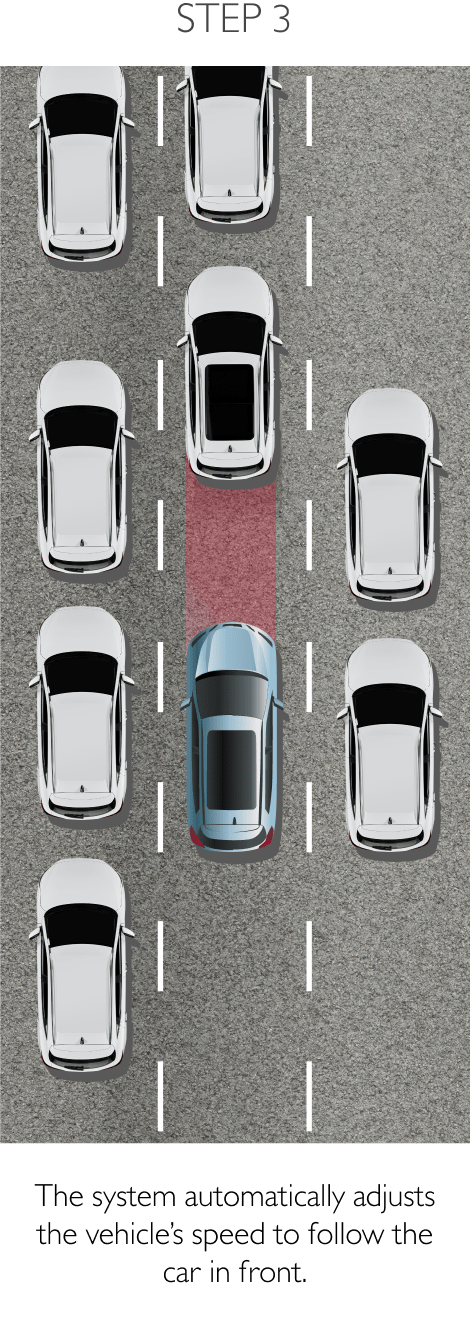
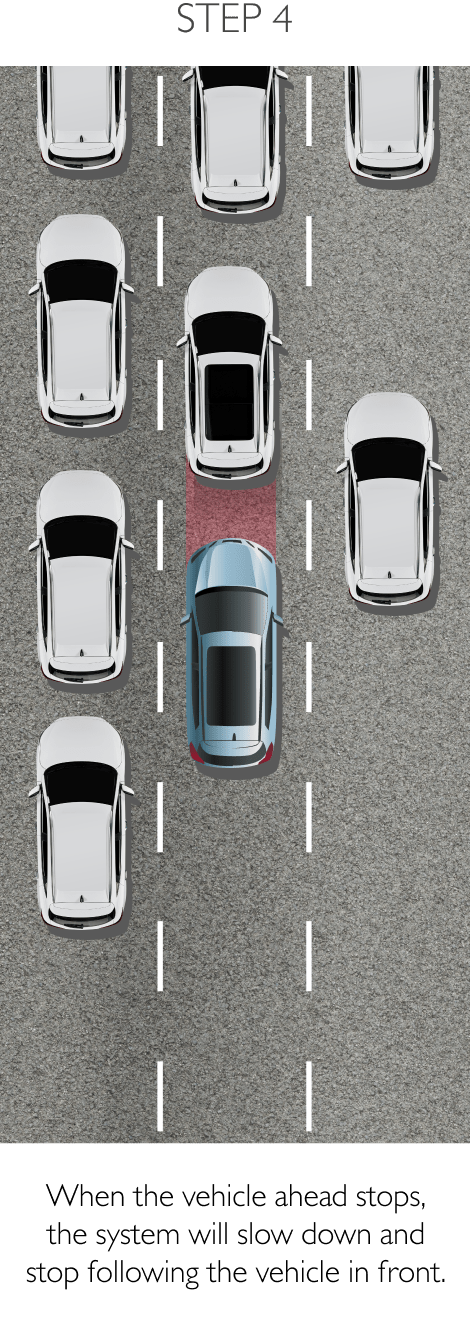
FDA is a system that primarily operates through the front sensor and will adjust settings and controls the should it detect worsening road and traffic conditions ahead. FDA is able to control the vehicle’s speed and increases driving comfort in heavy traffic and reduces the risk of colliding with the vehicle in front. The 4 sub-systems comprise the following.



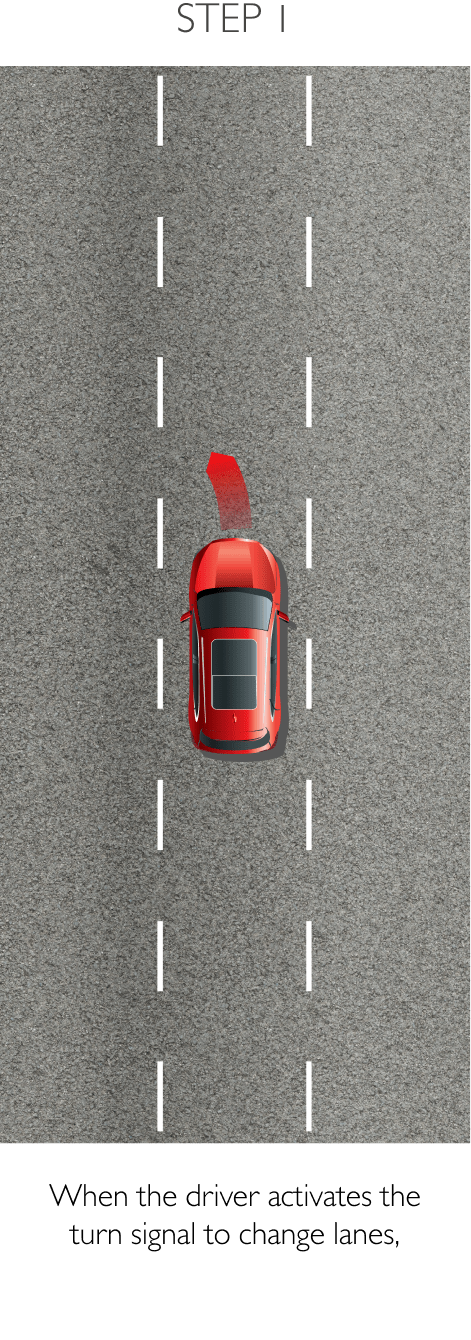
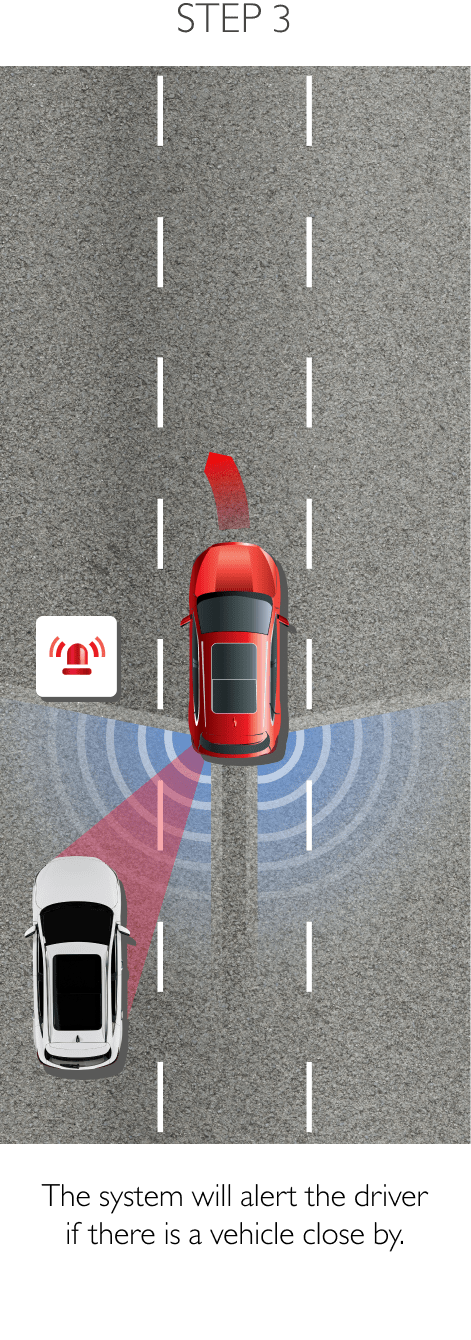
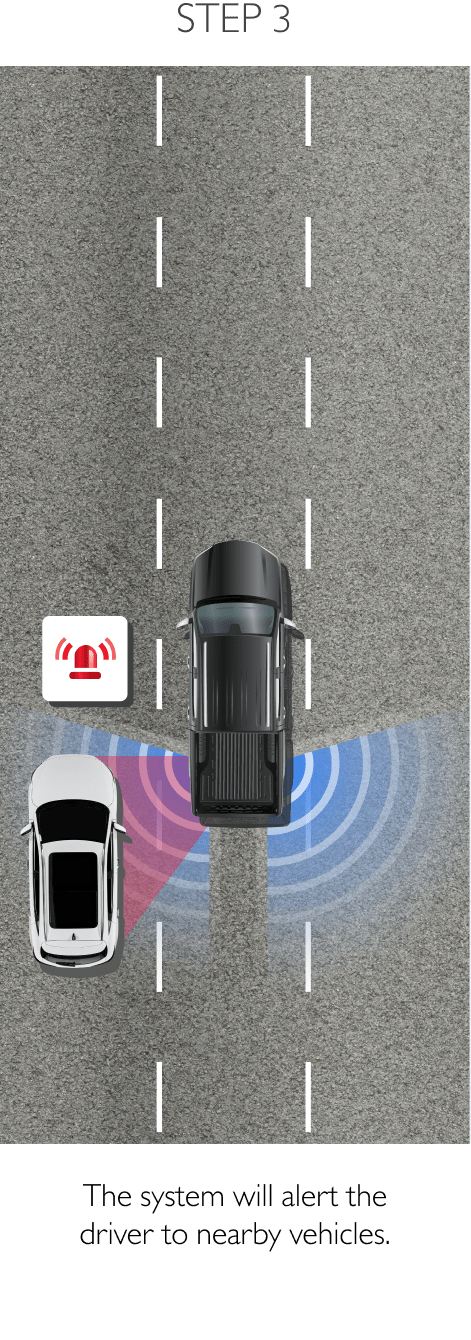
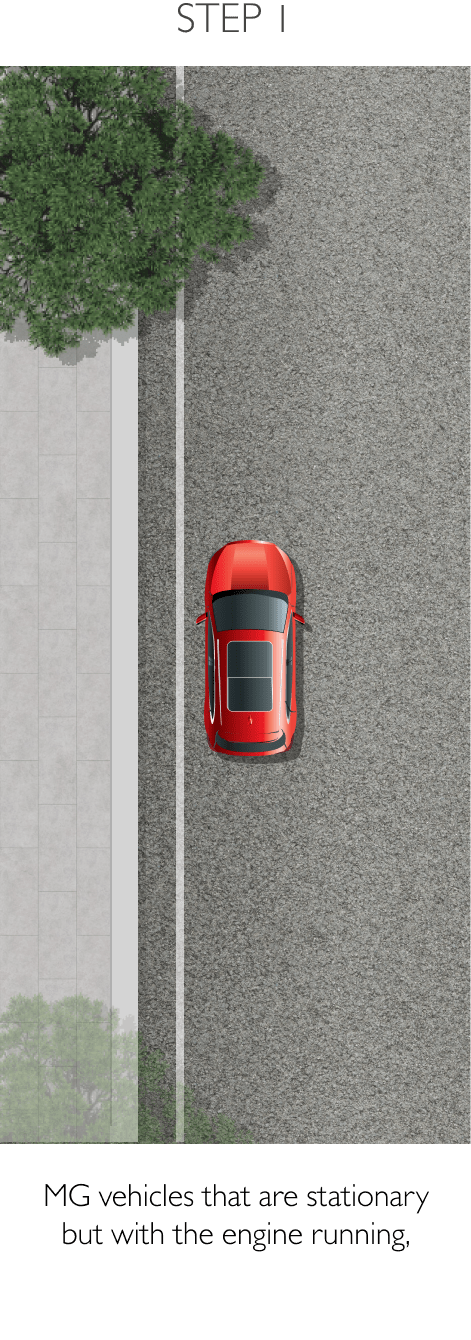
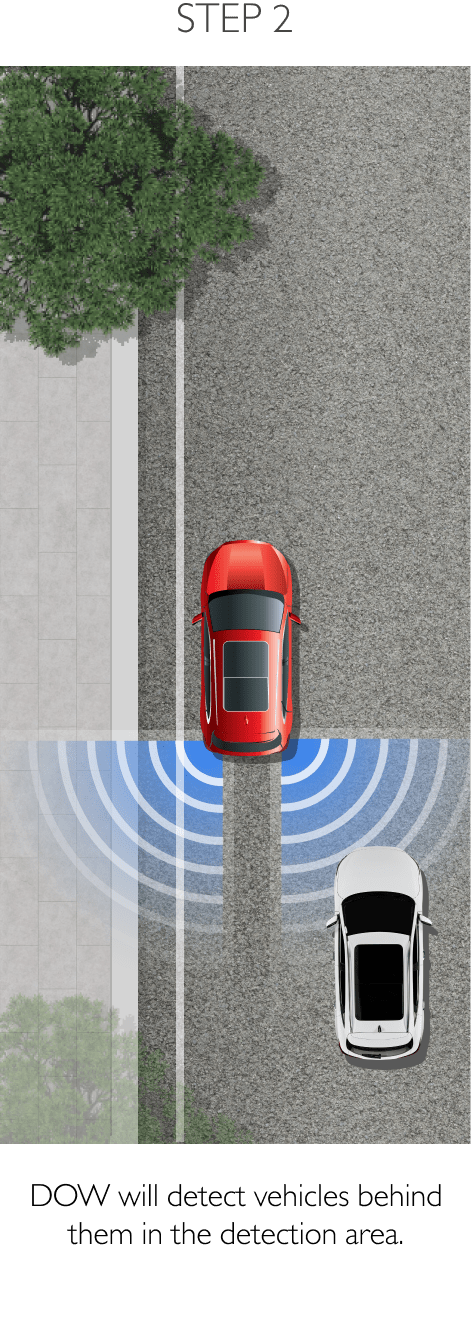
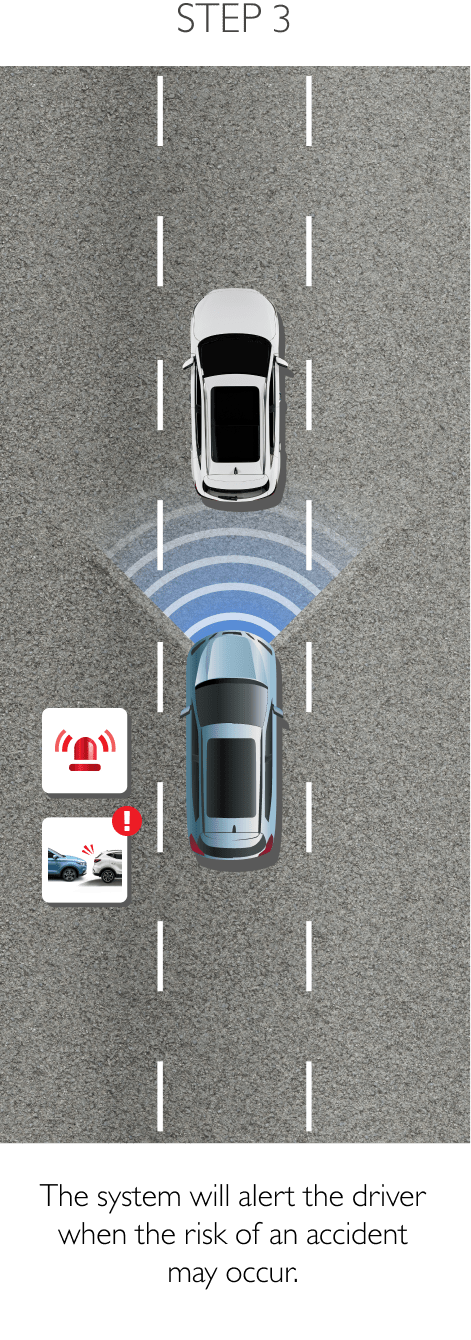
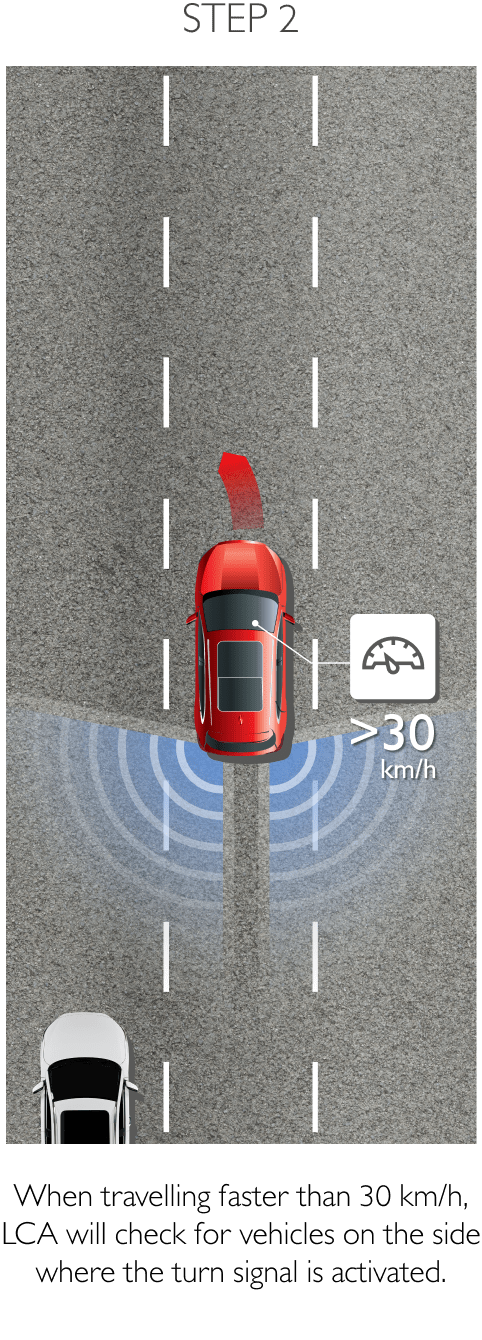
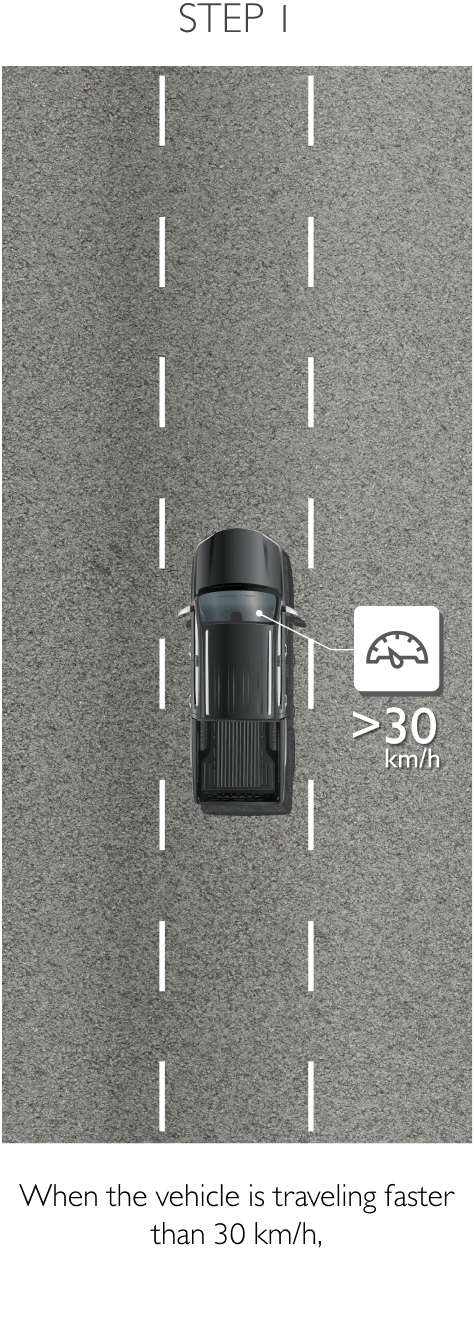
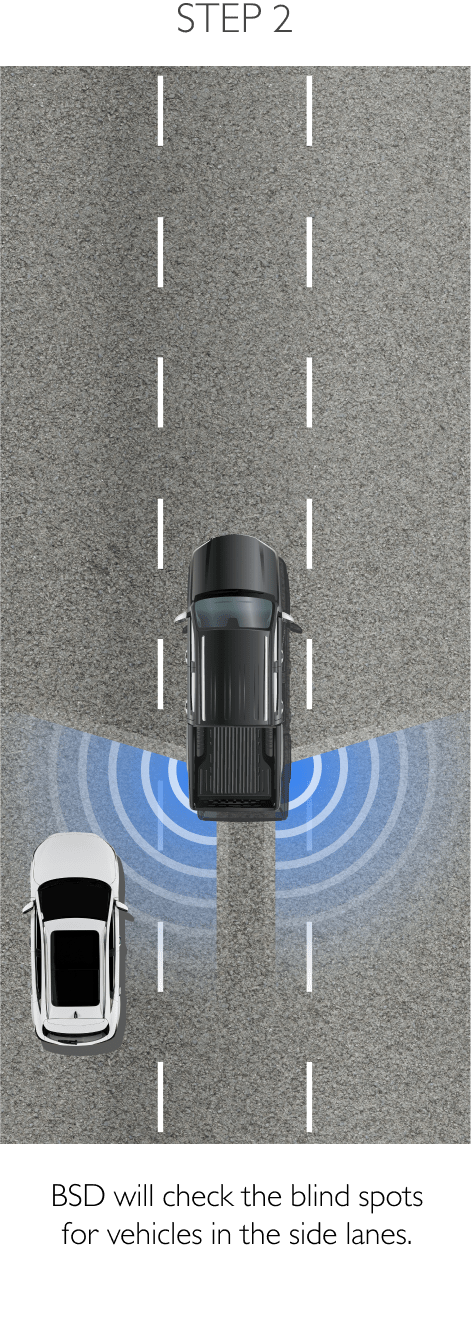
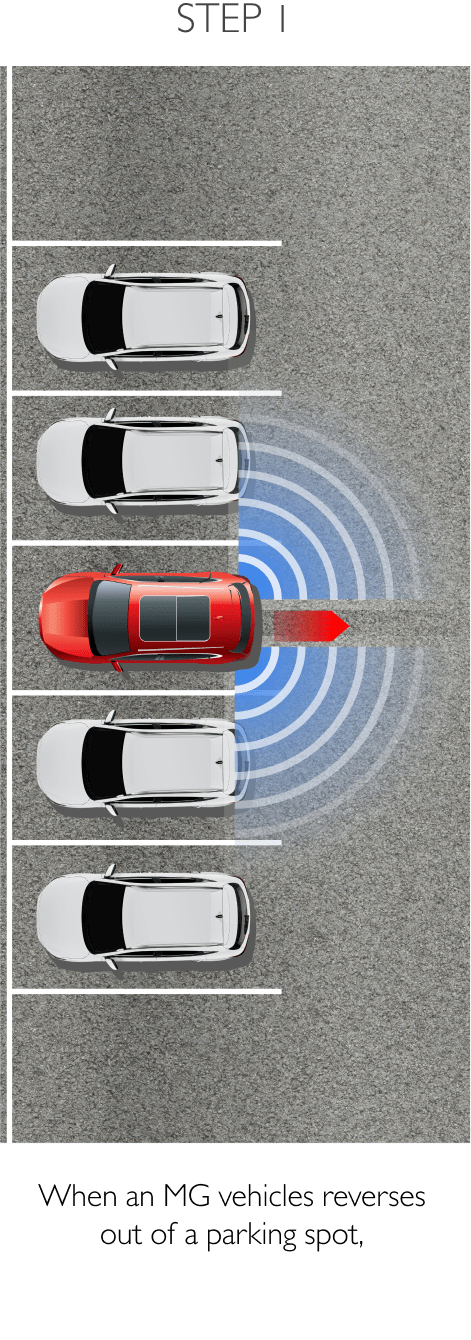
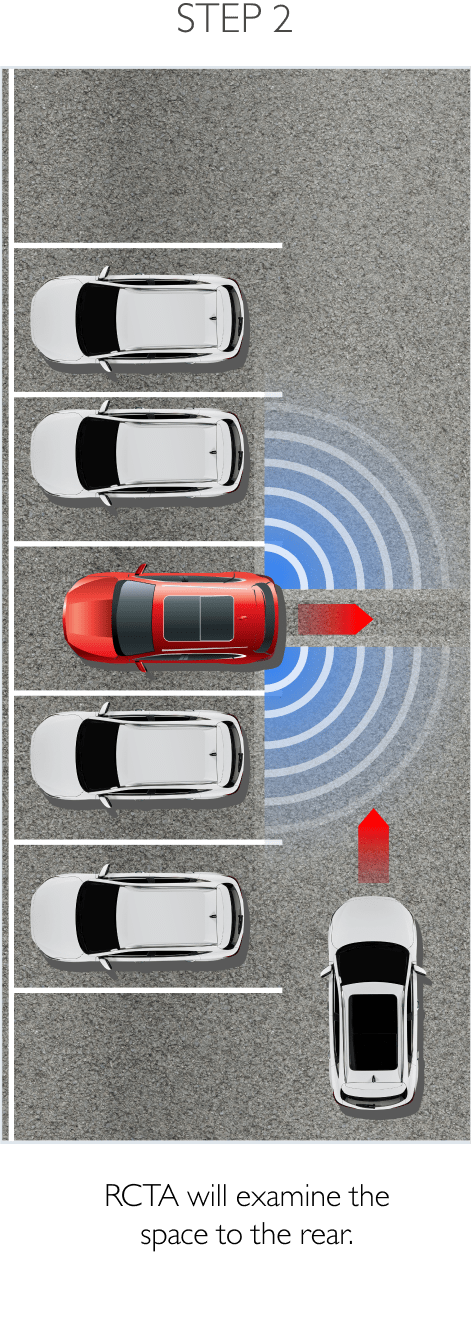
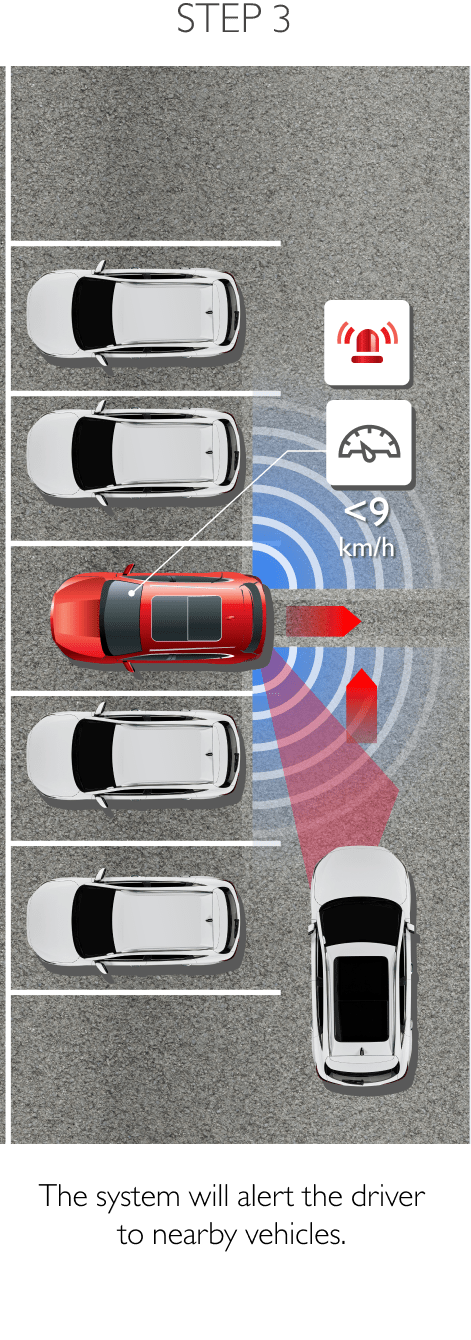
Using sensors installed to the rear, RDA helps prevent blind spots. The system can detect surrounding traffic conditions to both the vehicle’s sides and rear to cover every blind spot. When it detects an object or obstacle, RDA will alert the driver with cabin warning lights and flashing lights on the side mirror in which an object was detected. The system conveniently increases driver awareness and reduces the chance of collisions and accidents. RDA comprises the following 4 sub-systems.
Using sensors installed to the rear, RDA helps prevent blind spots. The system can detect surrounding traffic conditions to both the vehicle’s sides and rear to cover every blind spot. When it detects an object or obstacle, RDA will alert the driver with cabin warning lights and flashing lights on the side mirror in which an object was detected. The system conveniently increases driver awareness and reduces the chance of collisions and accidents. RDA comprises the following 4 sub-systems.